It's happened a few times that contributors misunderstood the guidelines, so they're clearly not clear enough. Hopefully this clarifies. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| cli | ||
| demos | ||
| docs | ||
| lib | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .envrc.recommended | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .watchmanconfig | ||
| AUTHORS | ||
| Cargo.lock | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| deny.toml | ||
| flake.lock | ||
| flake.nix | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| mkdocs.yml | ||
| poetry.lock | ||
| pyproject.toml | ||
| README.md | ||
| rustfmt.toml | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
Jujutsu VCS
Disclaimer
This is not a Google product. It is an experimental version-control system (VCS). I (Martin von Zweigbergk martinvonz@google.com) started it as a hobby project in late 2019. That said, this is now my full-time project at Google. My presentation from Git Merge 2022 has information about Google's plans. See the slides or the recording.
Introduction
Jujutsu is a Git-compatible
DVCS. It combines
features from Git (data model,
speed), Mercurial (anonymous
branching, simple CLI free from "the index",
revsets, powerful history-rewriting), and Pijul/Darcs
(first-class conflicts), with features not found in most
of them (working-copy-as-a-commit,
undo functionality, automatic rebase,
safe replication via rsync, Dropbox, or distributed file
system).
The command-line tool is called jj for now because it's easy to type and easy
to replace (rare in English). The project is called "Jujutsu" because it matches
"jj".
If you have any questions, please join us on Discord

Getting started
Follow the installation instructions to obtain and configure jj.
The best way to get started is probably to go through
the tutorial. Also see the
Git comparison, which includes a table of
jj vs. git commands.
As you become more familiar with Jujutsu, the FAQ may help.
Features
Compatible with Git
Jujutsu has two backends. One of them is a Git backend (the other is a native one 1). This lets you use Jujutsu as an alternative interface to Git. The commits you create will look like regular Git commits. You can always switch back to Git. The Git support uses the libgit2 C library.
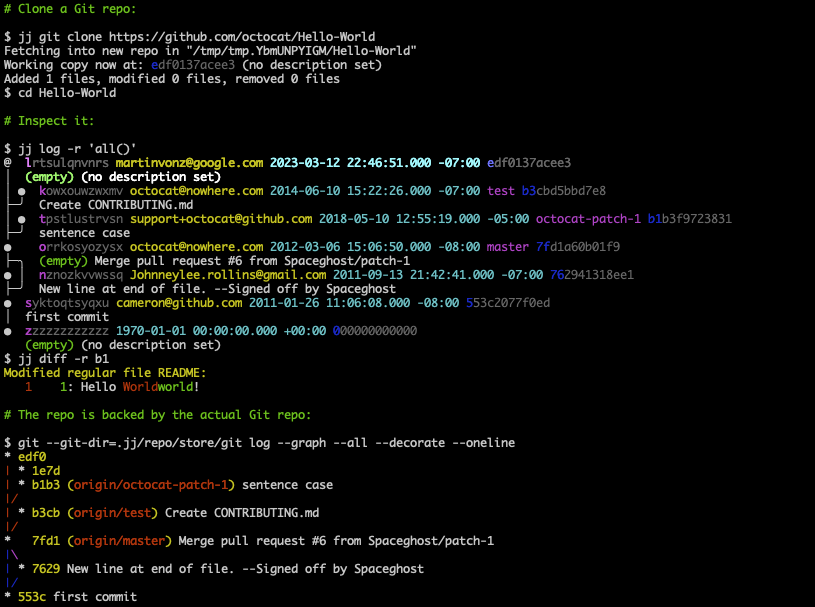
You can even have a "co-located" local
repository where you can
use both jj and git commands interchangeably.
The working copy is automatically committed
Jujutsu uses a real commit to represent the working copy. Checking out a commit results a new working-copy commit on top of the target commit. Almost all commands automatically amend the working-copy commit.
The working-copy being a commit means that commands never fail because the
working copy is dirty (no "error: Your local changes to the following
files..."), and there is no need for git stash. Also, because the working copy
is a commit, commands work the same way on the working-copy commit as on any
other commit, so you can set the commit message before you're done with the
changes.
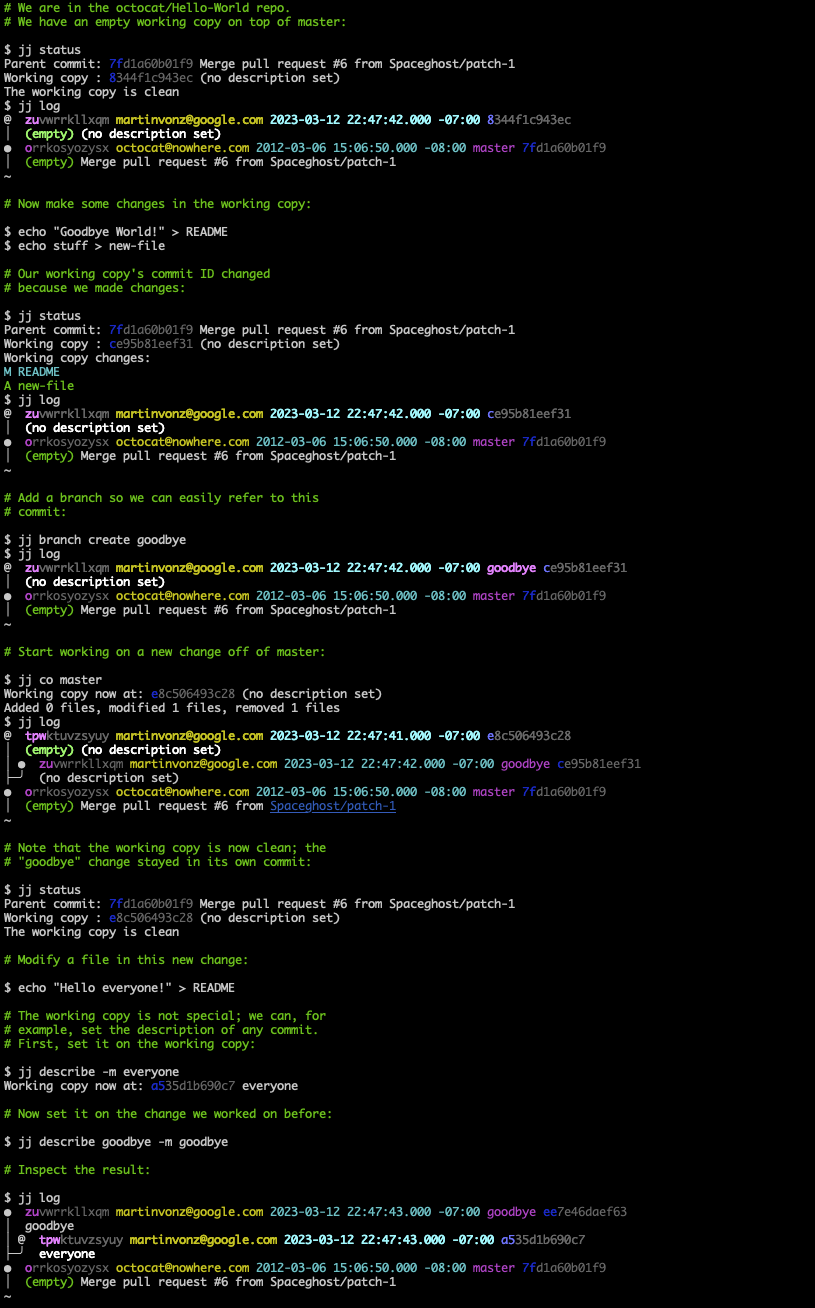
The repo is the source of truth
With Jujutsu, the working copy plays a smaller role than with Git. Commands
snapshot the working copy before they start, then they update the repo, and then
the working copy is updated (if the working-copy commit was modified). Almost
all commands (even checkout!) operate on the commits in the repo, leaving the
common functionality of snapshotting and updating of the working copy to
centralized code. For example, jj restore (similar to git restore) can
restore from any commit and into any commit, and jj describe can set the
commit message of any commit (defaults to the working-copy commit).
Entire repo is under version control
All operations you perform in the repo are recorded, along with a snapshot of the repo state after the operation. This means that you can easily revert to an earlier repo state, or to simply undo a particular operation (which does not necessarily have to be the most recent operation).

Conflicts can be recorded in commits
If an operation results in conflicts, information about those conflicts will be recorded in the commit(s). The operation will succeed. You can then resolve the conflicts later. One consequence of this design is that there's no need to continue interrupted operations. Instead, you get a single workflow for resolving conflicts, regardless of which command caused them. This design also lets Jujutsu rebase merge commits correctly (unlike both Git and Mercurial).
Basic conflict resolution:
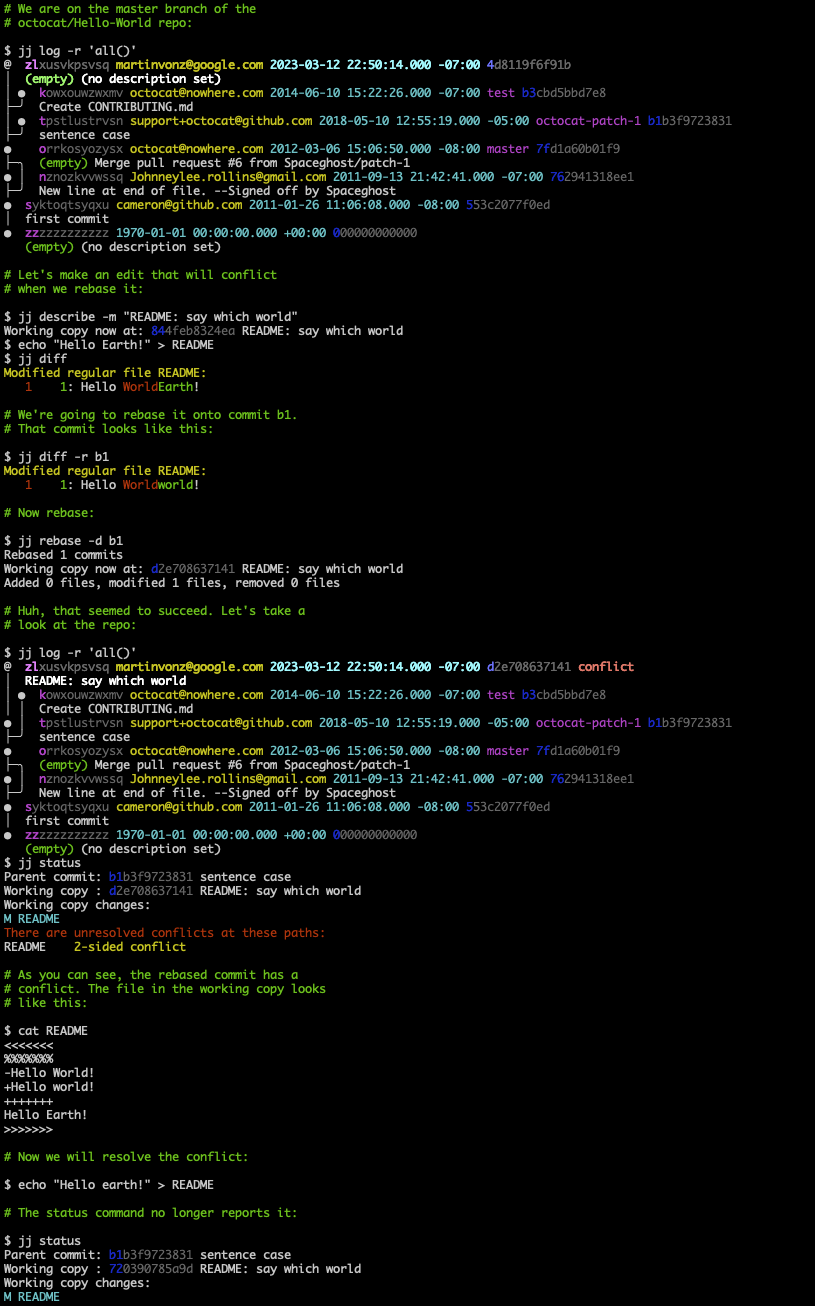
Juggling conflicts:

Automatic rebase
Whenever you modify a commit, any descendants of the old commit will be rebased onto the new commit. Thanks to the conflict design described above, that can be done even if there are conflicts. Branches pointing to rebased commits will be updated. So will the working copy if it points to a rebased commit.
Comprehensive support for rewriting history
Besides the usual rebase command, there's jj describe for editing the
description (commit message) of an arbitrary commit. There's also jj diffedit,
which lets you edit the changes in a commit without checking it out. To split
a commit into two, use jj split. You can even move part of the changes in a
commit to any other commit using jj move.
Status
The tool is quite feature-complete, but some important features like (the
equivalent of) git blame are not yet supported. There
are also several performance bugs. It's also likely that workflows and setups
different from what the core developers use are not well supported.
I (Martin von Zweigbergk) have almost exclusively used jj to develop the
project itself since early January 2021. I haven't had to re-clone from source
(I don't think I've even had to restore from backup).
There will be changes to workflows and backward-incompatible changes to the
on-disk formats before version 1.0.0. Even the binary's name may change (i.e.
away from jj). For any format changes, we'll try to implement transparent
upgrades (as we've done with recent changes), or provide upgrade commands or
scripts if requested.
Related work
There are several tools trying to solve similar problems as Jujutsu. See related work for details.
-
At this time, there's practically no reason to use the native backend. The backend exists mainly to make sure that it's possible to eventually add functionality that cannot easily be added to the Git backend. ↩︎





